- Spine Surgeon
- Spine
- Robotic Surgery
- Diseases
- Treatments
- News & Media
- Contact
Neuromuscular Disease in Adults & Children
Neuromuscular Disease in Adults
Adult neuromuscular disease refers to a range of different neuromuscular disorders such as Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, and various myopathies. These conditions not only cause difficulty walking but can also lead to spinal deformities, which can sometimes be very severe. Treatment typically involves a combination of medication and physiotherapy, and in rare cases, the use of braces. A small percentage of these patients may eventually require surgery.
Neuromuscular Disease in Children
Neuromuscular scoliosis in children is caused by various neuromuscular conditions such as cerebral palsy, spinal muscular atrophy, poliomyelitis, spinal muscle atrophy, spinal cord injuries, and others.
In these cases, the deformity—whether scoliosis or kyphosis—can lead to pain, loss of walking ability, or intolerance to sitting. Additionally, neuromuscular disease combined with scoliosis significantly affects pulmonary function, resulting in reduced lung capacity, shortness of breath, and respiratory infections.
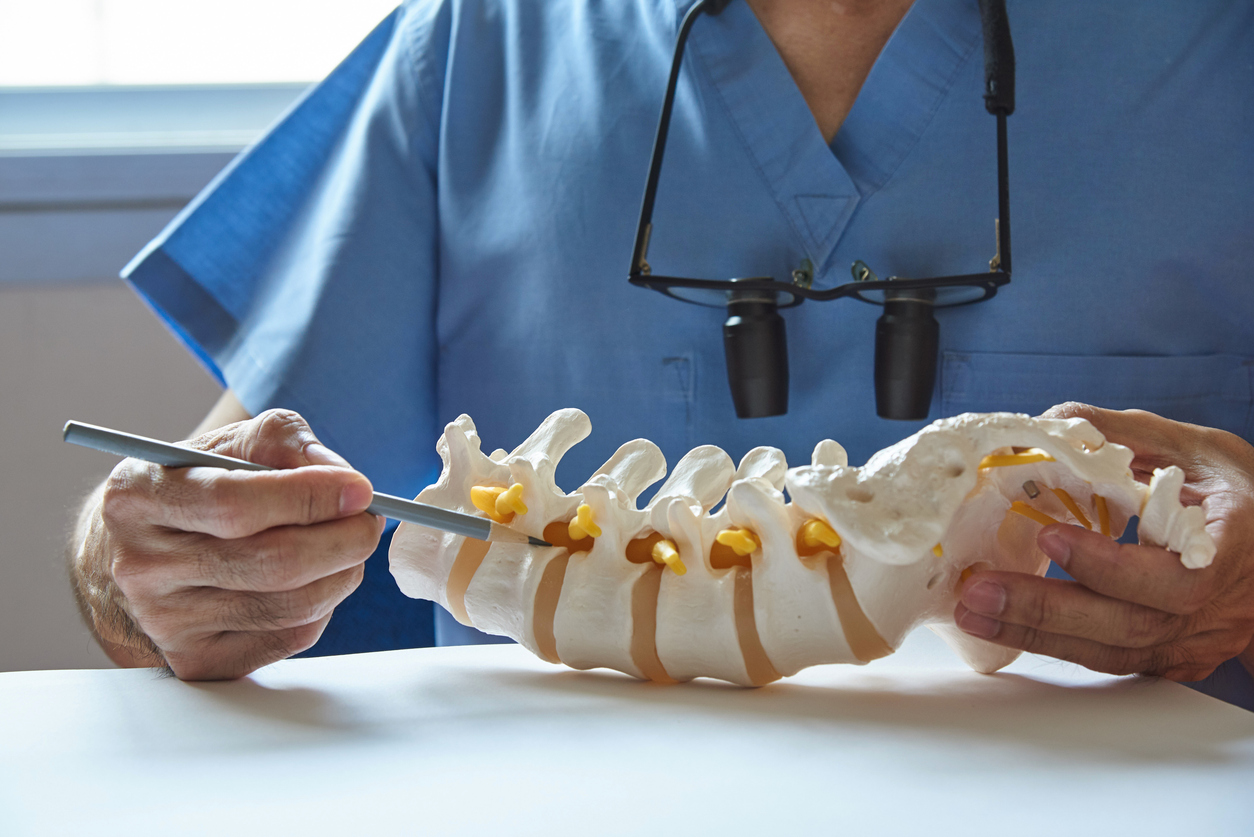
Management and Treatment
Treatment of neuromuscular scoliosis depends on the predominant problem, such as pain, difficulty maintaining a seated position, and the severity of the scoliosis.
Bracing is used for soft scoliosis curves under 50°. For patients who are non-ambulatory, modifications to wheelchairs can help them sit comfortably and maintain balance.
Surgical treatment is indicated for patients with progressive scoliosis that may lead to severe deformity in the future. Generally, surgery is recommended when the curve exceeds 50°, except in spinal muscular atrophy, where intervention is advised once scoliosis surpasses 20°. Surgery in these cases helps preserve lung function and the patients’ ability to walk for several more years.
Surgical procedures may be posterior only or a combination of anterior and posterior approaches. The success of these surgeries depends on achieving spinal balance to maintain the patient’s functionality and comfort, enabling them to lead a productive life despite their mobility challenges.
